In today’s world, sustainability and environmental responsibility have become paramount. The urgent need to address carbon emissions and reduce our collective carbon footprint is underscored by the alarming global carbon dioxide (CO2) level in the atmosphere, which has reached a record high of 414 parts per million (ppm). As businesses strive to adopt sustainable practices, digitalisation has emerged as a powerful tool for driving sustainability efforts and mitigating the impact of greenhouse gas emissions.
Understanding Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 Emissions
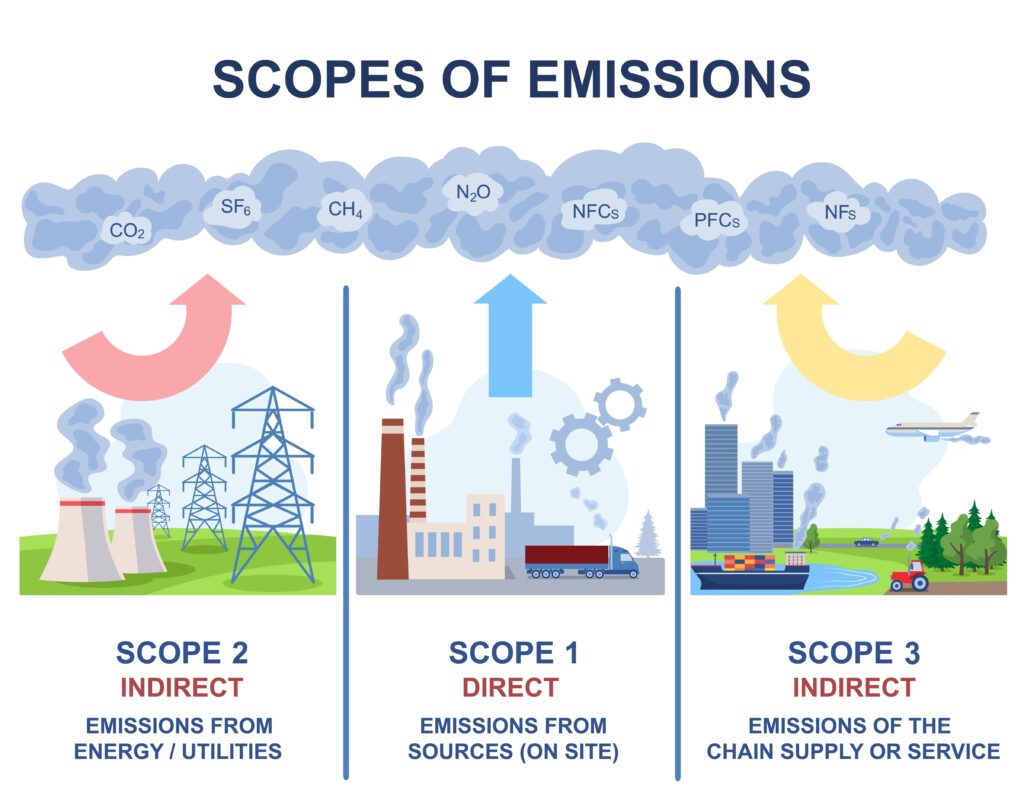
To effectively address carbon emissions, businesses must examine and manage their greenhouse gas emissions across three scopes: Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3. These emissions are categories of a globally recognised framework for tracking and managing greenhouse gas emissions.
Scope 1 Emissions
Scope 1 emissions encompass direct greenhouse gas emissions that result from sources owned or controlled by an organisation. These emissions are produced on-site or within the organisation’s operational boundaries. Examples of Scope 1 emissions include:
- Emissions from company-owned vehicles
- Emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels in on-site equipment, such as boilers or furnaces
- Emissions from chemical reactions within an organisation’s manufacturing processes
Scope 2 Emissions
Scope 2 emissions cover indirect greenhouse gas emissions associated with the generation of purchased or acquired electricity, steam, heating, or cooling. While organisations do not have direct control over the emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, it still contributes to their carbon footprint. Different methods are used to account for Scope 2 emissions:
- Location-Based: This method accounts for emissions based on the average emissions intensity of the electricity grid in the region where the organisation operates.
- Market-Based: This approach allows organisations to account for emissions associated with the specific energy sources they purchase, enabling the reporting of lower emissions when renewable energy certificates (RECs) are used to offset electricity consumption.
- Contract-Based: This approach is applied when organisations have long-term contracts with specific energy providers, accounting for emissions based on the contracted energy source.
Scope 3 Emissions
Scope 3 emissions are often the most challenging to measure and manage as they involve a wide range of sources throughout an organisation’s value chain. These emissions include:
- Supply Chain Emissions: Emissions associated with the production, transportation, and disposal of goods and services purchased by the organisation.
- Upstream Emissions: Emissions occurring in the early stages of a product’s life cycle, such as raw material extraction, processing, and transportation to manufacturing facilities.
- Downstream Emissions: Emissions occurring later in the product’s life cycle, such as distribution, use, and end-of-life disposal.
- Business Travel: Emissions from employee travel for work-related purposes, including air and road travel.
- Waste Generation: Emissions from the disposal and management of waste, including solid waste and wastewater.
The Importance of Digitisation for Sustainability
Digitisation, the process of converting analog information into digital format, has rapidly evolved from being a technological trend to a powerful tool for sustainability. By leveraging digital technologies, businesses can drive significant environmental improvements and achieve their sustainability goals. Here’s how digitisation contributes to sustainability efforts:
Optimising Energy Efficiency
Digitisation allows businesses to optimise their energy efficiency by monitoring and controlling energy consumption in real-time. By implementing digital technologies like sensors and smart systems, factories can identify energy inefficiencies and wasteful practices. This visibility enables them to make informed decisions and implement measures to reduce energy consumption, resulting in lower carbon emissions.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Digital tools enable factories to integrate cleaner and renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into their operations. By monitoring energy consumption and production, businesses can align their energy usage with the availability of renewable energy, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to emissions reduction.
Enhanced Process Efficiency
Digitisation streamlines and improves day-to-day business processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced resource consumption. By leveraging digital technologies, businesses can automate manual tasks, optimise workflows, and eliminate unnecessary steps, resulting in reduced energy and resource usage.
Supply Chain Optimisation
Digitalisation plays a crucial role in optimising supply chains, reducing inefficiencies, and streamlining operations. By implementing digital tools, businesses can shorten their value chains, improve logistics and transportation, and reduce emissions associated with the transportation and distribution of products.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The wealth of data generated through digitalisation enables businesses to make data-driven decisions. By analysing data from various sources, organisations can identify areas for improvement, optimise processes, and reduce waste, leading to enhanced resource efficiency and emissions reduction.
Emissions Monitoring and Reporting
Digitalisation facilitates accurate and real-time monitoring of emissions, enabling businesses to track and report their Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 emissions more precisely. Accurate data collection and reporting are crucial for demonstrating compliance with environmental regulations, building trust with stakeholders, and showcasing a commitment to sustainability.
WrxFlo stands at the forefront of integrating sustainability with digital solutions. WrxFlo’s comprehensive suite of tailored solutions unlocks the potential for significant efficiency gains across global supply chains. By identifying and bridging gaps in processes, data, and system functionality, WrxFlo ensures that sustainability is not just an add-on but a core component of the operational strategy. By leveraging the WrxFlo dashboard, companies can gain the critical insights into sustainability metrics, allowing them to actively monitor and manage their carbon footprint across Scope 1 , Scope 2 , and Scope 3 emissions. This real-time visibility into emissions data is crucial for setting targets, tracking progress, and making informed decisions that align with both environmental goals and business objectives. By leveraging WrxFlo’s expertise in engineering and software development, your organisation can drive sustainable practices with precision and confidence. Whether it’s improving efficiency in planning, warehousing, manufacturing, logistics, distribution, or the center of operations, WrxFlo’s custom solutions not only promise a 40-50% capacity improvement but also play a significant role in reducing costs and mitigating environmental impact. The path to sustainability is complex, but with WrxFlo, companies have a trusted ally to navigate the challenges and emerge as leaders in corporate environmental stewardship.
If you’re interested in learning how we can transform your business through digitalisation, contact us for a free non-contractual demo of the WrxFlo platform today. You are one step away from a completely digitalised future.




